v-for 指令的实现
在VueやReact这样的前端框架中,循环渲染是一个基本需求。在Vue中,这一功能通过v-for指令实现。本章我们将实现这一指令。
开发者接口
首先,我们来看看v-for指令的使用方式。v-for指令可以对数组、字符串、对象或范围进行循环。
以下是使用v-for指令的例子:
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
// 用于v-for循环的水果数组
fruits: [
{ id: 0, name: 'Apple', color: 'red' },
{ id: 1, name: 'Banana', color: 'yellow' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Cherry', color: 'red' },
],
// 输入字段的值
fruitName: '',
fruitColor: '',
}
},
methods: {
// 添加水果的方法
addFruit() {
const id = this.fruits.reduce((max, f) => Math.max(max, f.id), -1) + 1
this.fruits.push({ id, name: this.fruitName, color: this.fruitColor })
this.fruitName = ''
this.fruitColor = ''
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<h1>My Fruits</h1>
<ul>
<!-- 基本循环 -->
<li v-for="fruit in fruits">
{{ fruit.name }} - {{ fruit.color }}
</li>
</ul>
<h3>添加水果</h3>
<div>
<label> 名称: <input v-model="fruitName" /></label>
</div>
<div>
<label> 颜色: <input v-model="fruitColor" /></label>
</div>
<div>
<button @click="addFruit">添加</button>
</div>
<h3>使用索引的循环</h3>
<ul>
<!-- 使用索引的循环 -->
<li v-for="(fruit, i) in fruits">{{ i }}: {{ fruit.name }}</li>
</ul>
<h3>解构和其他变体</h3>
<ul>
<!-- 使用解构的循环 -->
<li v-for="{ id, name, color } in fruits">
ID: {{ id }}, 名称: {{ name }}, 颜色: {{ color }}
</li>
</ul>
<h3>嵌套循环</h3>
<ul>
<!-- 嵌套循环 -->
<li v-for="(fruit, i) in fruits">
{{ i }}: {{ fruit.name }}
<ul>
<li v-for="(value, key) in fruit">{{ key }}: {{ value }}</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</template>不用担心,我们会一步步实现这一功能。
我们需要实现的是能够编译如下代码:
<li v-for="(fruit, i) in fruits">{{ i }}: {{ fruit.name }}</li>编译成类似这样:
_renderList(fruits, (fruit, i) => {
return _createElementVNode("li", null, [
_createTextVNode(i + ": " + fruit.name)
])
})实际上,我们需要一个名为renderList的辅助函数来编译列表的渲染,功能类似于:
export function renderList(source, renderItem) {
const ret = []
if (Array.isArray(source) || typeof source === 'string') {
// 处理数组和字符串
const l = source.length
for (let i = 0; i < l; i++) {
ret.push(renderItem(source[i], i))
}
} else if (typeof source === 'number') {
// 处理数字范围
for (let i = 0; i < source; i++) {
ret.push(renderItem(i + 1, i))
}
} else if (typeof source === 'object') {
// 处理对象
if (source[Symbol.iterator]) {
// 处理可迭代对象
const arr = Array.from(source)
const l = arr.length
for (let i = 0; i < l; i++) {
ret.push(renderItem(arr[i], i))
}
} else {
// 处理普通对象
const keys = Object.keys(source)
const l = keys.length
for (let i = 0; i < l; i++) {
const key = keys[i]
ret.push(renderItem(source[key], key, i))
}
}
}
return ret
}不过,SFC的情况下需要考虑局部变量的问题。例如在下面的代码中:
<script>
export default {
methods: {
getFruits() {
return [...] // 返回水果数组
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<ul>
<li v-for="fruit in getFruits()">{{ fruit.name }}</li>
</ul>
</template>在这里,getFruits()需要通过this来访问,需要转换为this.getFruits()。但在v-for中定义的局部变量(如fruit)不应该加上前缀。
对于:
<li v-for="fruit in getFruits()">{{ fruit.name }}</li>应该编译为:
_renderList(this.getFruits(), (fruit) => {
return _createElementVNode("li", null, [
_createTextVNode(fruit.name)
])
})而不是:
_renderList(this.getFruits(), (fruit) => {
return _createElementVNode("li", null, [
_createTextVNode(this.fruit.name) /* fruit是局部变量,不应该有this前缀 */
])
})因此,我们需要某种方式来区分变量的作用域,以便在编译表达式时做出正确的转换。
AST的实现
我们需要为v-for定义相应的AST节点类型。
export const enum NodeTypes {
// ...现有代码...
FOR,
}
export interface ForNode extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.FOR
source: ExpressionNode
valueAlias: ExpressionNode | undefined
keyAlias: ExpressionNode | undefined
children: TemplateChildNode[]
parseResult: ForParseResult
}
// renderList的第二个参数使用回调函数,所以需要支持函数表达式
export interface FunctionExpression extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.JS_FUNCTION_EXPRESSION
params: ExpressionNode | string | (ExpressionNode | string)[] | undefined
returns?: TemplateChildNode | TemplateChildNode[] | JSChildNode
newline: boolean
}
// v-for的情况下,返回值是确定的,所以使用专门的AST表示
export interface ForIteratorExpression extends FunctionExpression {
returns: VNodeCall
}
export type JSChildNode =
| VNodeCall
| CallExpression
| ObjectExpression
| ArrayExpression
| ConditionalExpression
| ExpressionNode
| FunctionExpression 对于RENDER_LIST,我们也需要添加到runtimeHelpers中:
// runtimeHelpers.ts
// ...现有代码...
export const RENDER_LIST = Symbol()
export const helperNameMap: Record<symbol, string> = {
// ...现有代码...
[RENDER_LIST]: `renderList`,
// ...现有代码...
}关于ForParseResult,其定义在transform/vFor中:
export interface ForParseResult {
source: ExpressionNode
value: ExpressionNode | undefined
key: ExpressionNode | undefined
index: ExpressionNode | undefined
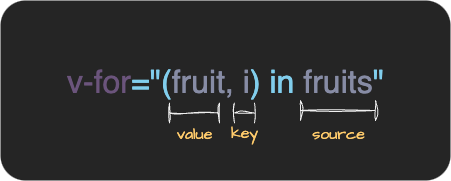
}这些属性分别代表什么呢?以v-for="(fruit, i) in fruits"为例:
- source:
fruits - value:
fruit - key:
i - index:
undefined
index是在v-for循环对象时用作第三个参数的属性。
可参考Vue的官方文档: https://ja.vuejs.org/guide/essentials/list.html#v-for-with-an-object
关于value,当使用如{ id, name, color, }这样的解构时,它会包含多个Identifier。
我们需要收集这些value、key、index中定义的标识符,并跳过前缀的添加。
codegen的实现
我们先实现codegen部分,因为这部分相对简单。主要有两个任务:处理NodeTypes.FOR和函数表达式的代码生成。
switch (node.type) {
case NodeTypes.ELEMENT:
case NodeTypes.FOR:
case NodeTypes.IF:
// ...现有代码...
case NodeTypes.JS_FUNCTION_EXPRESSION:
genFunctionExpression(node, context, option)
break
// ...现有代码...
}
function genFunctionExpression(
node: FunctionExpression,
context: CodegenContext,
option: CompilerOptions,
) {
const { push, indent, deindent } = context
const { params, returns, newline } = node
push(`(`, node)
if (isArray(params)) {
genNodeList(params, context, option)
} else if (params) {
genNode(params, context, option)
}
push(`) => `)
if (newline) {
push(`{`)
indent()
}
if (returns) {
if (newline) {
push(`return `)
}
if (isArray(returns)) {
genNodeListAsArray(returns, context, option)
} else {
genNode(returns, context, option)
}
}
if (newline) {
deindent()
push(`}`)
}
}这部分实现相对简单,现在已经完成了。
transformer的实现
准备工作
在实现transformer之前,我们需要做一些准备工作。
与v-on类似,v-for的processExpression执行时机有些特殊(需要收集本地变量),所以我们需要在transformExpression中跳过它:
export const transformExpression: NodeTransform = (node, ctx) => {
if (node.type === NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION) {
node.content = processExpression(node.content as SimpleExpressionNode, ctx)
} else if (node.type === NodeTypes.ELEMENT) {
for (let i = 0; i < node.props.length; i++) {
const dir = node.props[i]
if (
dir.type === NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE &&
dir.name !== 'for'
) {
// ...现有代码...
}
}
}
}收集标识符
现在我们来考虑如何收集标识符。
我们需要处理的不仅仅是简单的标识符如fruit,还有解构表达式如{ id, name, color }。为此,我们需要使用TreeWalker。
目前,processExpression会搜索标识符并添加_ctx前缀,但我们现在需要的是收集标识符而不添加前缀。
首先,我们需要一个地方来存储收集到的标识符。为了方便codegen等操作,我们给AST节点添加一个属性来存储标识符列表:
export interface SimpleExpressionNode extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
content: string
isStatic: boolean
identifiers?: string[]
}
export interface CompoundExpressionNode extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.COMPOUND_EXPRESSION
children: (
| SimpleExpressionNode
| CompoundExpressionNode
| InterpolationNode
| TextNode
| string
)[]
identifiers?: string[]
}我们需要在processExpression中收集标识符,并将收集到的标识符添加到transformer的上下文中,以便跳过前缀的添加。
目前添加/删除标识符的函数只接受单个字符串标识符,我们需要修改它以支持{ identifier: string[] }:
export interface TransformContext extends Required<TransformOptions> {
// ...现有代码...
addIdentifiers(exp: ExpressionNode | string): void
removeIdentifiers(exp: ExpressionNode | string): void
// ...现有代码...
}
const context: TransformContext = {
// ...现有代码...
addIdentifiers(exp) {
if (!isBrowser) {
if (isString(exp)) {
addId(exp)
} else if (exp.identifiers) {
exp.identifiers.forEach(addId)
} else if (exp.type === NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION) {
addId(exp.content)
}
}
},
removeIdentifiers(exp) {
if (!isBrowser) {
if (isString(exp)) {
removeId(exp)
} else if (exp.identifiers) {
exp.identifiers.forEach(removeId)
} else if (exp.type === NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION) {
removeId(exp.content)
}
}
},
// ...现有代码...
}现在,我们在processExpression中实现标识符收集功能:
export function processExpression(
node: SimpleExpressionNode,
ctx: TransformContext,
asParams = false,
) {
// ...
if (isSimpleIdentifier(rawExp)) {
const isScopeVarReference = ctx.identifiers[rawExp]
if (
!asParams &&
!isScopeVarReference
) {
node.content = rewriteIdentifier(rawExp)
}
return node
// ...
}
}对于简单标识符,到此为止。但还需要处理其它情况。
我们将使用babelUtils中实现的walkIdentifiers。
由于我们是处理函数参数中定义的本地变量,所以需要将它们转换为"函数参数"的形式,并让walkIdentifier搜索Function的param:
// 当asParams为true时,将表达式转换为函数参数形式
const source = `(${rawExp})${asParams ? `=>{}` : ``}`walkIdentifiers的实现稍微复杂一些:
export function walkIdentifiers(
root: Node,
onIdentifier: (node: Identifier) => void,
knownIds: Record<string, number> = Object.create(null),
parentStack: Node[] = [],
) {
// ...
;(walk as any)(root, {
// prettier-ignore
enter(node: Node, parent: Node | undefined) {
parent && parentStack.push(parent);
if (node.type === "Identifier") {
const isLocal = !!knownIds[node.name];
const isRefed = isReferencedIdentifier(node, parent!, parentStack);
if (!isLocal && isRefed) {
onIdentifier(node);
}
} else if (isFunctionType(node)) {
// 在函数中收集参数标识符到knownIds
walkFunctionParams(node, (id) =>
markScopeIdentifier(node, id, knownIds)
);
}
},
})
}
export const isFunctionType = (node: Node): node is Function => {
return /Function(?:Expression|Declaration)$|Method$/.test(node.type)
}这里的主要工作是,当节点是函数时,遍历其参数并收集标识符到knownIds中。
在调用walkIdentifiers的地方,我们定义knownIds并传递给walkIdentifiers,让它收集标识符。收集完成后,在生成CompoundExpression时使用knownIds生成identifiers。
const knownIds: Record<string, number> = Object.create(ctx.identifiers)
walkIdentifiers(
ast,
node => {
node.name = rewriteIdentifier(node.name)
ids.push(node as QualifiedId)
},
knownIds, // 传递knownIds
parentStack,
)
// ...
ret.identifiers = Object.keys(knownIds) // 使用knownIds生成identifiers
return retwalkFunctionParams和markScopeIdentifier的功能相对简单:遍历参数并将Node.name添加到knownIds中。
export function walkFunctionParams(
node: Function,
onIdent: (id: Identifier) => void,
) {
for (const p of node.params) {
for (const id of extractIdentifiers(p)) {
onIdent(id)
}
}
}
function markScopeIdentifier(
node: Node & { scopeIds?: Set<string> },
child: Identifier,
knownIds: Record<string, number>,
) {
const { name } = child
if (node.scopeIds && node.scopeIds.has(name)) {
return
}
if (name in knownIds) {
knownIds[name]++
} else {
knownIds[name] = 1
}
;(node.scopeIds || (node.scopeIds = new Set())).add(name)
}现在我们可以收集标识符了,接下来使用这些功能实现transformFor,完成v-for指令!
transformFor
与v-if类似,v-for也是结构性指令,所以我们使用createStructuralDirectiveTransform来实现。
下面的代码包含详细的注释,但我建议你在查看这些代码前先尝试自己实现:
// 类似于v-if的实现,这是基本框架
// 在适当的地方执行processFor,并在适当的地方生成codegenNode
// processFor是最复杂的部分
export const transformFor = createStructuralDirectiveTransform(
'for',
(node, dir, context) => {
return processFor(node, dir, context, forNode => {
// 按预期调用renderList生成代码
const renderExp = createCallExpression(context.helper(RENDER_LIST), [
forNode.source,
]) as ForRenderListExpression
// 生成v-for容器Fragment的codegenNode
forNode.codegenNode = createVNodeCall(
context,
context.helper(FRAGMENT),
undefined,
renderExp,
) as ForCodegenNode
// codegen处理(在processFor内完成parse和identifiers收集后执行)
return () => {
const { children } = forNode
const childBlock = (children[0] as ElementNode).codegenNode as VNodeCall
renderExp.arguments.push(
createFunctionExpression(
createForLoopParams(forNode.parseResult),
childBlock,
true /* 强制换行 */,
) as ForIteratorExpression,
)
}
})
},
)
export function processFor(
node: ElementNode,
dir: DirectiveNode,
context: TransformContext,
processCodegen?: (forNode: ForNode) => (() => void) | undefined,
) {
// 解析v-for表达式
// 在parseResult阶段,各节点的identifiers已收集完成
const parseResult = parseForExpression(
dir.exp as SimpleExpressionNode,
context,
)
const { addIdentifiers, removeIdentifiers } = context
const { source, value, key, index } = parseResult!
const forNode: ForNode = {
type: NodeTypes.FOR,
loc: dir.loc,
source,
valueAlias: value,
keyAlias: key,
parseResult: parseResult!,
children: [node],
}
// 将节点替换为forNode
context.replaceNode(forNode)
if (!context.isBrowser) {
// 将收集到的identifiers添加到context中
value && addIdentifiers(value)
key && addIdentifiers(key)
index && addIdentifiers(index)
}
// 生成代码(这样可以跳过本地变量前缀的添加)
const onExit = processCodegen && processCodegen(forNode)
return () => {
value && removeIdentifiers(value)
key && removeIdentifiers(key)
index && removeIdentifiers(index)
if (onExit) onExit()
}
}
// 使用正则表达式解析v-for表达式
const forAliasRE = /([\s\S]*?)\s+(?:in|of)\s+([\s\S]*)/
const forIteratorRE = /,([^,\}\]]*)(?:,([^,\}\]]*))?$/
const stripParensRE = /^\(|\)$/g
export interface ForParseResult {
source: ExpressionNode
value: ExpressionNode | undefined
key: ExpressionNode | undefined
index: ExpressionNode | undefined
}
export function parseForExpression(
input: SimpleExpressionNode,
context: TransformContext,
): ForParseResult | undefined {
const loc = input.loc
const exp = input.content
const inMatch = exp.match(forAliasRE)
if (!inMatch) return
const [, LHS, RHS] = inMatch
const result: ForParseResult = {
source: createAliasExpression(
loc,
RHS.trim(),
exp.indexOf(RHS, LHS.length),
),
value: undefined,
key: undefined,
index: undefined,
}
if (!context.isBrowser) {
result.source = processExpression(
result.source as SimpleExpressionNode,
context,
)
}
let valueContent = LHS.trim().replace(stripParensRE, '').trim()
const iteratorMatch = valueContent.match(forIteratorRE)
const trimmedOffset = LHS.indexOf(valueContent)
if (iteratorMatch) {
valueContent = valueContent.replace(forIteratorRE, '').trim()
const keyContent = iteratorMatch[1].trim()
let keyOffset: number | undefined
if (keyContent) {
keyOffset = exp.indexOf(keyContent, trimmedOffset + valueContent.length)
result.key = createAliasExpression(loc, keyContent, keyOffset)
if (!context.isBrowser) {
// 非浏览器模式下,设置asParams为true,收集key的identifiers
result.key = processExpression(result.key, context, true)
}
}
if (iteratorMatch[2]) {
const indexContent = iteratorMatch[2].trim()
if (indexContent) {
result.index = createAliasExpression(
loc,
indexContent,
exp.indexOf(
indexContent,
result.key
? keyOffset! + keyContent.length
: trimmedOffset + valueContent.length,
),
)
if (!context.isBrowser) {
// 非浏览器模式下,设置asParams为true,收集index的identifiers
result.index = processExpression(result.index, context, true)
}
}
}
}
if (valueContent) {
result.value = createAliasExpression(loc, valueContent, trimmedOffset)
if (!context.isBrowser) {
// 非浏览器模式下,设置asParams为true,收集value的identifiers
result.value = processExpression(result.value, context, true)
}
}
return result
}
function createAliasExpression(
range: SourceLocation,
content: string,
offset: number,
): SimpleExpressionNode {
return createSimpleExpression(
content,
false,
getInnerRange(range, offset, content.length),
)
}
export function createForLoopParams(
{ value, key, index }: ForParseResult,
memoArgs: ExpressionNode[] = [],
): ExpressionNode[] {
return createParamsList([value, key, index, ...memoArgs])
}
function createParamsList(
args: (ExpressionNode | undefined)[],
): ExpressionNode[] {
let i = args.length
while (i--) {
if (args[i]) break
}
return args
.slice(0, i + 1)
.map((arg, i) => arg || createSimpleExpression(`_`.repeat(i + 1), false))
}现在,只要实现编译后代码中包含的renderList函数和注册transformer,v-for就应该可以正常工作了!
让我们来看一下实际效果:

看起来一切顺利!
到这里的源代码: GitHub
 The chibivue Book
The chibivue Book